Introduzione
A vehicle’s exhaust system performs two vital functions: controlling noise and reducing harmful emissions. The muffler reduces the sound generated by engine combustion, while the convertitore catalitico a tre vie transforms toxic gases into less harmful substances. Together, they ensure vehicles run efficiently, quietly, and with minimal environmental impact. Understanding how these two components work and interact reveals the intricate balance between performance, acoustics, and emission control in modern automotive engineering.
1. The Purpose of a Muffler and Catalytic Converter in the Exhaust System
Every combustion cycle inside an engine produces exhaust gases and loud sound waves. Without a muffler, these pressure waves would create an unbearable noise as they exit the tailpipe. Similarly, without a convertitore catalitico a tre vie, the exhaust would release dangerous gases such as carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides.
The muffler and the catalytic converter are key partners in the exhaust system. While the muffler focuses on acoustic control, the catalytic converter focuses on chemical conversion. Together, they make cars quieter and cleaner.
2. Internal Design and Working Principles of Mufflers
A muffler uses a network of chambers, perforated tubes, and sound-absorbing materials to manage noise. The primary goal is to create destructive interference, where sound waves cancel each other out. The structure includes:
- Inlet and outlet pipes: Channels that guide exhaust gases through the muffler.
- Baffles and chambers: Redirect and reflect sound waves for cancellation.
- Fiberglass or acoustic packing: Absorbs remaining sound energy.
When the high-pressure exhaust enters the muffler, the waves bounce off the internal walls. The overlapping of these waves causes them to neutralize each other, reducing noise before gases exit the system.
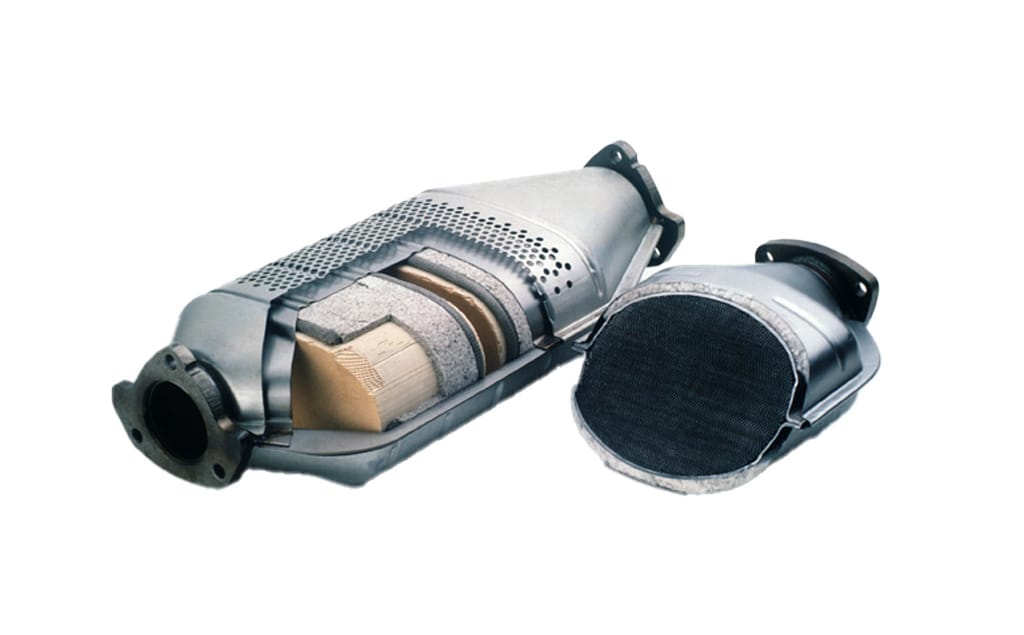
3. How the Three Way Catalytic Converter Works
IL convertitore catalitico a tre vie (TWC) is the most important emission control device in modern gasoline vehicles. It performs three simultaneous chemical reactions:
- Ossidazione del monossido di carbonio (CO) into carbon dioxide (CO₂).
- Ossidazione degli idrocarburi (HC) into carbon dioxide and water (H₂O).
- Riduzione degli ossidi di azoto (NOx) into nitrogen (N₂) and oxygen (O₂).
These reactions take place on a ceramic honeycomb substrate coated with precious metals such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium. The high surface area allows efficient conversion even at high temperatures.

4. Comparison Between Muffler and Three Way Catalytic Converter
| Componente | Funzione | Main Principle | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Muffler | Reduces sound waves | Acoustic reflection and interference | Lowers noise pollution |
| Convertitore catalitico a tre vie | Converts toxic gases | Chemical oxidation and reduction | Reduces air pollution |
Although they serve different purposes, both are crucial for environmental sustainability and regulatory compliance.
5. Integration of Mufflers and Catalytic Converters in Exhaust Systems
Modern automotive engineers often integrate the muffler and convertitore catalitico a tre vie in a single exhaust assembly to improve performance and reduce weight. This integration shortens the exhaust path, improves heat retention, and allows faster catalyst warm-up—essential for emission efficiency.
This design also simplifies maintenance, as both the acoustic and emission functions are combined in one unit. The result is an exhaust system that is lighter, cleaner, and more efficient.
6. Acoustic Science Behind Mufflers
The science of sound reduction in mufflers involves both destructive interference E sound absorption. Destructive interference occurs when two sound waves with opposite phases meet, canceling each other out. The muffler’s chambers are designed to reflect sound waves precisely so that this cancellation occurs at targeted frequencies.
Some mufflers also include resonance tubes tuned to specific engine frequencies, acting like musical instruments that neutralize sound peaks. Materials like fiberglass further absorb residual noise energy by converting it into heat.
7. Technological Advances in Emission and Noise Control
Recent innovations have led to active exhaust systems, which use sensors and actuators to control noise levels dynamically. Electronic noise cancellation now complements traditional muffler design, creating adjustable exhaust sounds based on driving modes.
Meanwhile, catalytic converters have evolved into high-efficiency three way systems that achieve over 90% reduction in CO, HC, and NOx emissions. Advanced substrates, such as metallic monoliths, improve heat transfer and lower startup emissions.
8. Muffler and Catalytic Converter Maintenance
Both the muffler and the catalytic converter require proper maintenance for optimal performance. A damaged muffler can cause loud noise, while a clogged catalytic converter can reduce engine efficiency and increase emissions.
Maintenance tips:
- Regularly inspect the exhaust system for rust, leaks, or cracks.
- Avoid using leaded fuels, which can poison the catalyst.
- Replace worn gaskets and clamps to prevent exhaust leaks.
Proper care ensures these components last longer and function effectively, maintaining both performance and compliance.
9. Environmental and Regulatory Importance
Global emission standards such as Euro 6 and U.S. EPA Tier 3 require vehicles to meet strict limits on pollutants and noise levels. Mufflers and three way catalytic converters play a central role in achieving these targets. Together, they reduce environmental impact by lowering both air and noise pollution.
As electric and hybrid vehicles grow in popularity, noise and emission control systems continue to evolve. Even EVs use specialized mufflers for sound tuning and safety sound generation.
10. Conclusion
The muffler and convertitore catalitico a tre vie form a symbiotic relationship within the vehicle’s exhaust system. The muffler manages acoustic energy, while the catalytic converter manages chemical energy. Together, they transform raw engine output into a cleaner and quieter experience for both drivers and the environment.
Future innovations will likely focus on lightweight materials, smart sound control, and higher-efficiency catalysts, driving the automotive industry toward a quieter and greener future.