Giới thiệu
Every modern vehicle operates with a complex network of mechanical and chemical systems designed to control emissions and improve engine efficiency. Among these, the bộ chuyển đổi xúc tác stands out as one of the most critical components of the automotive exhaust system. It plays a central role in reducing harmful gases, converting toxic exhaust pollutants into less harmful compounds.
But how exactly does the catalytic converter fit into the exhaust system? What is the difference between a bộ chuyển đổi xúc tác ba chiều, Một mission control converter, and other automotive emission converters? Understanding these questions not only enhances your technical knowledge but also deepens your appreciation for the sophisticated technology that keeps vehicles eco-friendly and compliant with global emission standards.
1. Overview of the Exhaust System
The exhaust system in a vehicle is an integrated pathway that channels and treats gases produced by combustion. It removes the residual gases generated in the engine cylinders and ensures that they are safely expelled from the tailpipe.
A typical exhaust system includes several major parts:
- Exhaust manifold
- Oxygen sensors
- Bộ chuyển đổi xúc tác
- Resonator
- Bộ giảm thanh
- Tailpipe
Each component has a defined role, and together, they maintain efficient gas flow, control noise, and minimize environmental pollution.
| Thành phần | Chức năng | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Exhaust Manifold | Collects exhaust gases from engine cylinders | Attached to the engine block |
| Oxygen Sensor | Measures oxygen level in exhaust gases | Before and after catalytic converter |
| Bộ chuyển đổi xúc tác | Converts toxic gases into harmless compounds | Between engine and muffler |
| Resonator & Muffler | Reduce exhaust noise | Rear section of the exhaust system |
| Tailpipe | Releases treated gases | End of exhaust system |
2. The Catalytic Converter: The Heart of Emission Control
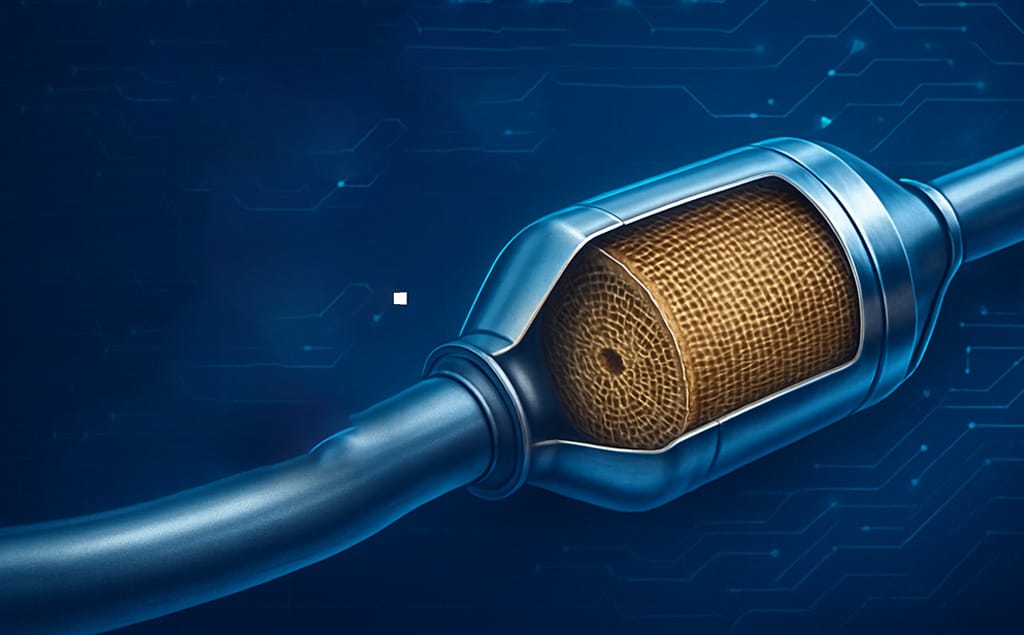
MỘT bộ chuyển đổi xúc tác là một emission control device that uses a combination of heat, chemistry, and precious metals to transform toxic gases into safer ones. This process is known as catalytic oxidation and reduction, or “redox.”
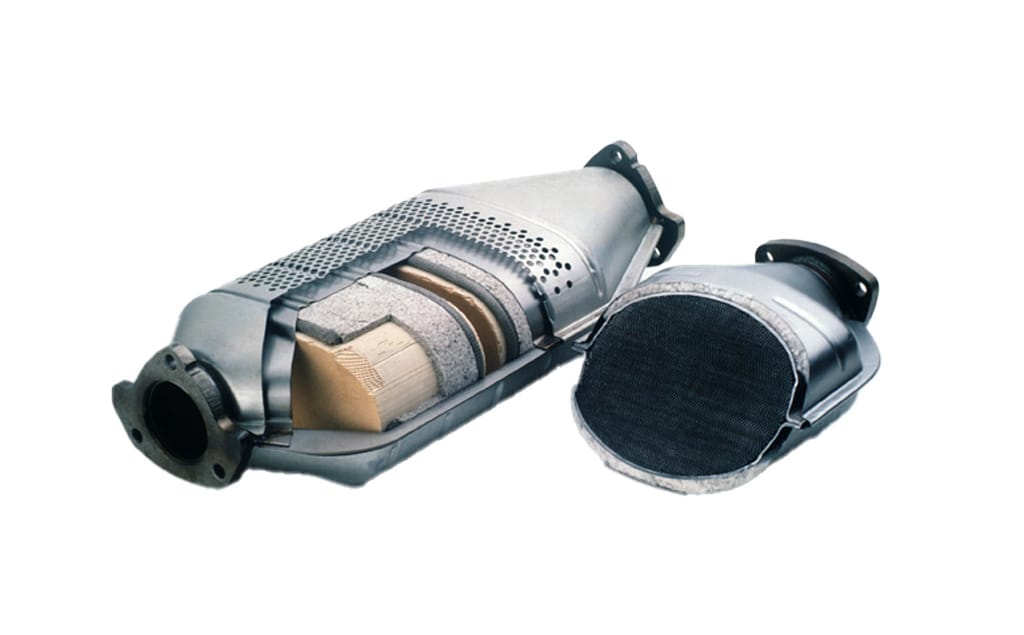
The converter is typically made of a stainless-steel housing containing a cấu trúc tổ ong coated with precious metals such as bạch kim (Pt), palađi (Pd) và rhodi (Rh). These metals serve as chất xúc tác, meaning they accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed.
When the hot exhaust gases flow through the converter:
- Carbon monoxide (CO) is oxidized into carbon dioxide (CO₂).
- Hydrocarbons (HC) are burned into water vapor (H₂O) and CO₂.
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are reduced to nitrogen (N₂) and oxygen (O₂).
This is the core function that makes a bộ chuyển đổi xúc tác ba chiều so valuable.
3. The Relationship Between Catalytic Converter and Exhaust System
Yes, the catalytic converter is indeed part of the exhaust system. It sits strategically between the engine and the muffler, positioned to handle gases immediately after combustion but before they are released into the atmosphere.
Its role in the exhaust system can be summarized as:
- Purification: Cleans the exhaust gases by breaking down pollutants.
- Integration: Works with oxygen sensors to monitor air-fuel ratio.
- Protection: Prevents harmful compounds from damaging the muffler and other components.
In modern vehicles, the catalytic converter acts as the mission control center of the exhaust system, continuously balancing chemical reactions to achieve optimal emission levels.
4. Different Types of Catalytic Converters
Automotive emission control technology has evolved, resulting in several types of converters:
| Kiểu | Chức năng chính | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Two Way Catalytic Converter | Converts CO and HC | Older gasoline engines |
| Bộ chuyển đổi xúc tác ba chiều | Converts CO, HC, and NOx | Modern gasoline vehicles |
| Chất xúc tác oxy hóa diesel (DOC) | Converts CO and HC in diesel engines | Xe chạy bằng dầu diesel |
| Giảm xúc tác chọn lọc (SCR) | Reduces NOx using urea (DEF) | Heavy-duty diesel systems |
| Mission Control Converter | Advanced system integrating sensors & catalysts | High-performance vehicles |
Các bộ chuyển đổi xúc tác ba chiều remains the most popular due to its efficiency in controlling all three major pollutants simultaneously. Meanwhile, mission control converters Và automotive emission converters represent the next generation, designed for tighter emission regulations and smarter engine feedback systems.
5. Materials and Design Innovations
The efficiency of a catalytic converter depends heavily on its substrate structure Và lớp phủ xúc tác. Modern converters use ceramic or metallic honeycomb cores, which increase surface area and promote better chemical reactions.
Innovations include:
- Thin-walled substrates to reduce weight and improve heat transfer.
- Advanced catalyst layering to maximize conversion rates.
- Integrated temperature sensors for real-time monitoring.
These design upgrades are critical for achieving Euro 6 and EPA Tier 3 emission standards.
6. How Three Way Catalytic Converters Work
MỘT bộ chuyển đổi xúc tác ba chiều (TWC) performs three simultaneous reactions:
- Quá trình oxy hóa Carbon Monoxide (CO) → CO₂
- Quá trình oxy hóa hydrocarbon (HC) → CO₂ + H₂O
- Giảm oxit nitơ (NOx) → N₂ + O₂
To function properly, the TWC requires a stoichiometric air-fuel ratio (14.7:1). Oxygen sensors constantly send feedback to the engine control unit (ECU) to maintain this balance.
When the air-fuel mixture is too rich (too much fuel), the converter reduces NOx more efficiently. When it’s too lean (too much air), it oxidizes CO and HC more efficiently. This delicate balance is what keeps the emission output within regulatory limits.

7. Common Problems and Maintenance
While catalytic converters are designed to last the life of the vehicle, several issues can affect performance:
- Clogging or Melting due to unburned fuel or overheating.
- Sự ô nhiễm from oil or coolant leaks.
- Sensor Failure leading to improper air-fuel mixture.
- Thiệt hại vật lý from road impact or theft.
Routine inspections and engine maintenance are crucial to preserving converter efficiency. Drivers should also avoid using leaded fuel, which permanently damages the catalyst.
8. The Role of Mission Control and Advanced Emission Converters
Modern vehicles equipped with mission control converters go beyond simple chemical reactions. These systems integrate real-time data from multiple sensors, adjusting catalyst activity and temperature dynamically.
This approach improves:
- Cold start performance (reducing initial emissions)
- Fuel economy
- Durability under high load conditions
Advanced automotive emission converters are now designed with AI-assisted control systems that predict engine behavior and pre-adjust catalytic activity — an innovation that defines the future of emission technology.
9. Environmental and Legal Importance
Catalytic converters are not just technical devices—they are environmental safeguards. By transforming toxic gases, they play a major role in:
- Reducing urban smog
- Lowering greenhouse emissions
- Meeting governmental emission regulations
Many countries legally require catalytic converters on all road vehicles. Tampering with or removing one can result in heavy fines and environmental penalties.
Phần kết luận
In summary, the bộ chuyển đổi xúc tác is an indispensable part of the automotive exhaust system, serving as the main line of defense against harmful emissions. Whether in the form of a bộ chuyển đổi xúc tác ba chiều, Một mission control converter, or a modern bộ chuyển đổi khí thải ô tô, its purpose remains the same: to protect the environment and ensure that vehicles operate efficiently and responsibly.
The future of emission control will continue to evolve with smarter converters, better materials, and intelligent systems — all working together to create a cleaner and more sustainable world of transportation.