Introduction
The three way catalytic converter serves as the primary defense against vehicle pollution. Every modern Ford vehicle relies on this component to transform toxic gases into harmless substances. This device sits within the exhaust system. It manages carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides simultaneously. Maintaining this part ensures your Ford stays fuel-efficient and legally compliant. Neglecting the three way catalytic converter leads to expensive repairs and engine performance drops. This guide provides a scientific look at maintaining your Ford’s emission system. We will explore preventative measures and diagnostic techniques. Follow these steps to maximize the lifespan of your vehicle’s exhaust components.

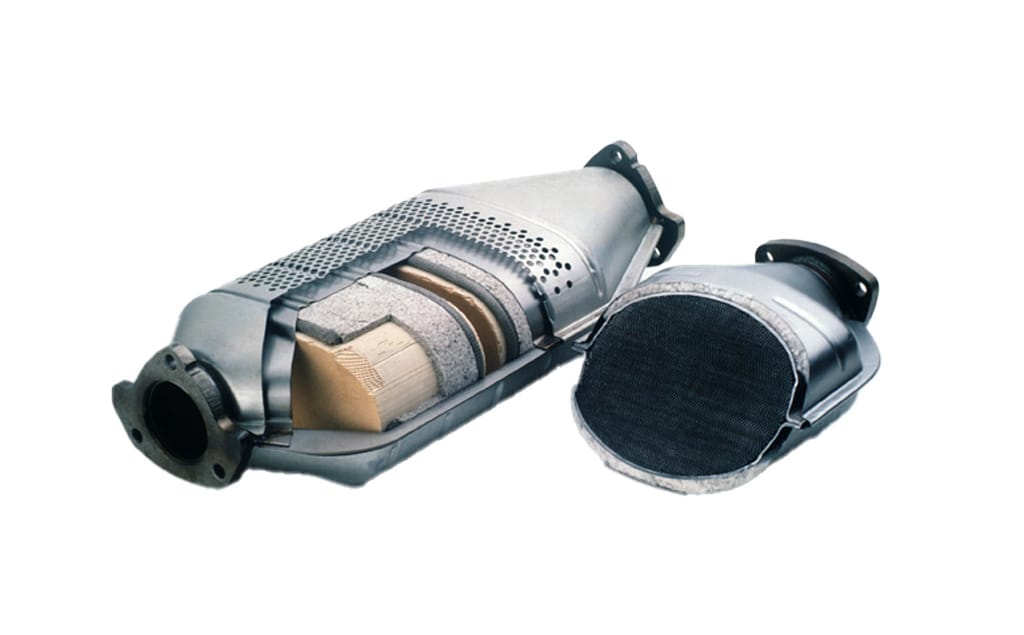
The Science of the Three Way Catalytic Converte
A three way catalytic converter uses a complex internal structure. A ceramic honeycomb core provides a massive surface area. Manufacturers coat this core with precious metals like platinum, palladium, and rhodium. These metals act as catalysts for chemical reactions. The “three way” designation refers to the three specific pollutants the device neutralizes. It oxidizes carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons. It also reduces nitrogen oxides.
The device requires high heat to function. This “light-off” temperature usually exceeds 400 degrees Celsius. Without reaching this temperature, the chemical reactions fail. Ford engines use precise fuel management to reach this heat quickly. However, various factors can disrupt this delicate balance.
Core Preventative Maintenance Strategies
1. Prioritize Fuel Quality and Grade
Your Ford’s manual specifies a certain fuel grade. Always follow this recommendation strictly. Low-quality fuels often contain high levels of sulfur or lead. These contaminants “poison” the precious metal coating inside the three way catalytic converter. Lead bonds to the catalyst sites. This prevents the exhaust gases from touching the metals. Consequently, the converter loses its efficiency. Use Top Tier gasoline whenever possible. This fuel contains additives that keep injectors clean. Clean injectors ensure a perfect air-fuel ratio. This protects the three way catalytic converter from unburnt fuel.
2. Optimize Your Driving Patterns
Frequent short trips damage the exhaust system. During short drives, the engine never reaches its optimal operating temperature. The three way catalytic converter stays cold. Water vapor also accumulates in the exhaust pipe. This moisture mixes with carbon to form acidic compounds. These compounds corrode the internal structure. If you drive short distances often, schedule a weekly highway run. Drive at highway speeds for at least twenty minutes. This allows the system to reach high temperatures. It burns off soot and moisture effectively.
3. Immediate Resolution of Engine Faults
The engine and the three way catalytic converter work as a single unit. A fault in the engine directly impacts the converter. Misfires represent the greatest threat. A misfire sends raw gasoline into the hot exhaust. This fuel ignites inside the three way catalytic converter. This event creates extreme temperatures. It can melt the ceramic honeycomb structure. You must fix “Check Engine” lights immediately. Address intake leaks and vacuum leaks promptly. These issues cause lean or rich conditions. Both states stress the catalyst.
4. Component Synchronization and Health
Monitor the health of the oxygen sensors. These sensors tell the engine computer how much fuel to inject. A “lazy” sensor provides slow data. This leads to fuel imbalances. Replace spark plugs according to Ford’s service intervals. Worn plugs cause incomplete combustion. Check the fuel injectors for leaks. A leaking injector drips fuel into the cylinder after the engine shuts off. This fuel eventually reaches the three way catalytic converter. Ensure the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve functions correctly. The EGR valve reduces nitrogen oxide production. This takes the workload off the converter.
5. High RPM Thermal Cleaning
Occasionally, you should “drive the car hard.” Find a safe road and maintain 2500 to 3000 RPM for several miles. This creates high-velocity exhaust flow. The increased heat helps oxidize carbon deposits. It clears minor clogs within the honeycomb. This process acts as a “self-cleaning” cycle for the three way catalytic converter. Do not exceed speed limits. Simply use a lower gear to maintain higher engine speeds.
Identifying Potential Failure Signs
You must recognize early symptoms of a failing three way catalytic converter. Early detection saves the engine from secondary damage.
- Pungent Odors: A “rotten egg” smell indicates a problem. This sulfur smell means the converter is not processing hydrogen sulfide. It suggests the catalyst is overwhelmed or damaged.
- Performance Degradation: Clogged converters create backpressure. The engine struggles to breathe. You will notice sluggish acceleration. The vehicle may feel “choked” at high speeds.
- Idling Instability: A restricted exhaust flow causes rough idling. The engine may stall when you stop at a light.
- Audible Rattling: If the ceramic core breaks, it rattles. You will hear a metallic sound from under the car. This usually happens during startup or acceleration.
- Dashboard Warnings: The On-Board Diagnostics (OBD-II) system monitors efficiency. The “Check Engine” light will trigger if efficiency drops below a threshold. Code P0420 is the most common indicator for Ford vehicles.
Advanced Maintenance Data and Comparisons
The following tables help categorize maintenance tasks and diagnostic data.
Table 1: Catalyst Health Indicators
| Parameter | Healthy Range | Failure Sign |
|---|---|---|
| Inlet Temperature | 400°F – 600°F (at idle) | Below 350°F |
| Outlet Temperature | Higher than Inlet (by 100°F+) | Lower than Inlet |
| Backpressure | Below 1.5 PSI at idle | Above 3.0 PSI |
| Oxygen Sensor 2 Signal | Steady/Flat Voltage | Rapid Fluctuations |
Table 2: Common Contaminants and Sources
| Contaminant | Source | Effect on Three Way Catalytic Converter |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Oil | Worn Piston Rings | Coats the catalyst in phosphorus/zinc |
| Coolant | Leaking Head Gasket | “Silica poisoning” of the ceramic core |
| Unburnt Fuel | Ignition Misfire | Thermal meltdown of the honeycomb |
| Sulfur | Low-Quality Fuel | Temporary reduction in efficiency |
Critical Prohibitions for Ford Owners
To protect your three way catalytic converter, avoid these specific actions:
- Extended Cranking: Do not crank the engine for more than 10 seconds. This pumps unburnt fuel into the exhaust.
- Disconnected Wires: Never run the engine with a disconnected spark plug wire. This ensures raw fuel reaches the catalyst.
- Manual Starting: Avoid push-starting or tow-starting the vehicle. These methods often result in fuel flooding the exhaust system.
- Hazardous Parking: Never park your Ford on dry grass or tall weeds. The three way catalytic converter operates at extreme temperatures. It can easily ignite dry vegetation and start a fire.

Professional Diagnostic Techniques
If you suspect a failure, seek a professional technician. They use specialized tools to confirm the state of the three way catalytic converter.
Thermal Delta Analysis
Technicians use infrared thermometers. They measure the temperature at the converter’s inlet and outlet. A functional three way catalytic converter creates an exothermic reaction. This means the outlet should be significantly hotter than the inlet. If the outlet is cooler, the catalyst is inactive.
Exhaust Backpressure Testing
Technicians remove the upstream oxygen sensor. They install a pressure gauge in its place. This measures how much resistance the exhaust faces. High pressure indicates a physical blockage inside the three way catalytic converter.
Digital Scan Tool Analysis
Technicians use OBD-II scanners to view “live data.” They look at the “fuel trim” values. They also watch the downstream oxygen sensor waveform. A healthy converter shows a very steady voltage on the rear sensor. A failing converter shows a sensor that “mimics” the front sensor.
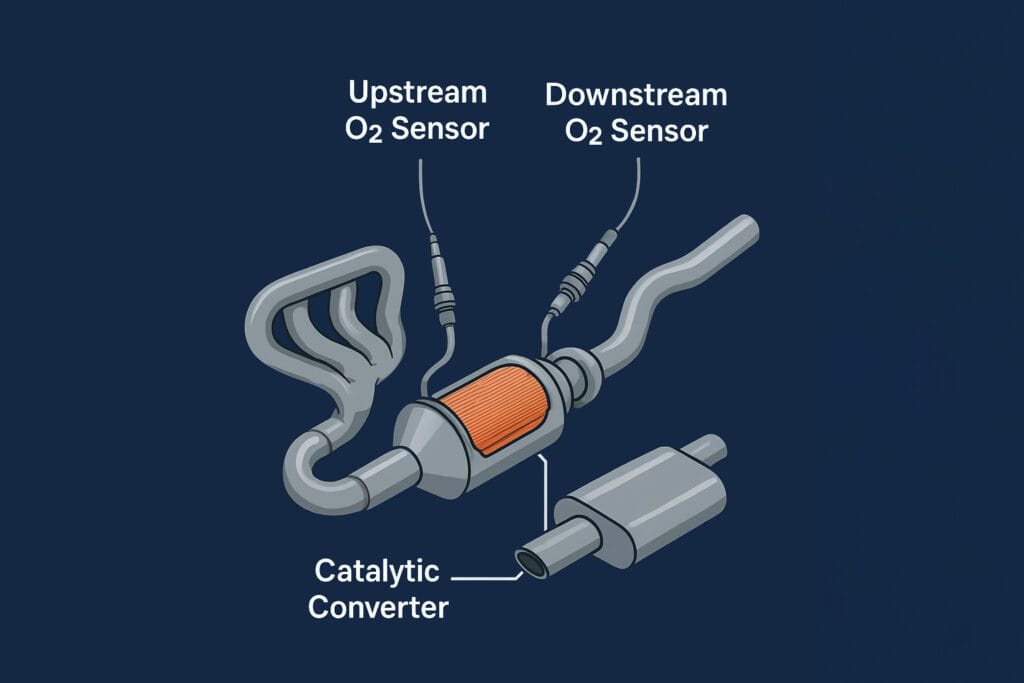
The Role of Oxygen Sensors in Catalyst Health
Oxygen sensors act as the eyes of the engine control module. Most Ford vehicles use at least two sensors for each three way catalytic converter. The upstream sensor measures the exhaust gas before it enters the converter. This sensor controls the air-fuel mixture. The downstream sensor monitors the gas after it leaves the converter. It specifically checks the oxygen storage capacity of the catalyst.
A faulty upstream sensor causes the engine to run “rich.” This means the engine burns too much fuel. The excess fuel eventually destroys the three way catalytic converter. Replacing an oxygen sensor is cheap. Replacing a converter is expensive. Always prioritize sensor maintenance to save the converter. Modern Ford systems are very sensitive. They require genuine Motorcraft sensors for the best performance.
Environmental and Legal Impact of the Catalyst
The three way catalytic converter is not just a performance part. It is a legal requirement under the Clean Air Act. Driving with a failed converter increases your vehicle’s carbon footprint significantly. It releases smog-forming compounds into the atmosphere. Most states require an emissions test for registration renewal. A failed three way catalytic converter will result in an immediate test failure.
Furthermore, removing the converter is illegal in many jurisdictions. Federal law prohibits the tampering with or removal of emission control devices. Maintaining your converter keeps you compliant with the law. It also protects the air quality in your community. Ford engineers designed the system to last over 100,000 miles. With proper care, many converters last the life of the vehicle.
Conclusion
The three way catalytic converter remains a vital component of your Ford’s ecosystem. Proper maintenance requires a holistic approach to engine health. You must use high-quality fuel and address engine codes immediately. Avoid short trips to prevent moisture buildup. Use highway driving to thermally clean the system. Recognize the signs of failure like foul smells and power loss. By following these scientific maintenance protocols, you extend the life of your exhaust system. This saves money and protects the environment. A well-maintained Ford performs better and retains its value longer.







